We design and audit digital products to meet WCAG and EAA standards.

Accessible design benefits everyone. It removes barriers, improves usability, and helps your product reach more people. Accessibility is built into every project we design and develop.
Increased market share
People with disabilities travel, eat at restaurants, own cars, purchase items for family and friends. By employing accessibility tools you can capture all your potential customers, including 10-15% market share you might be missing.
Legal compliance
By adhering to accessibility standards and regulations, businesses mitigate the risk of legal actions, fines, and reputational damage.
Boosted SEO
Investments in digital accessibility are ultimately reflected in your website’s search rankings. Google’s own mission statement is “to organize the world's information and make it universally accessible and useful”.
Future-Proofing
Digital inclusion contribute to building a more resilient and future-proof business that can adapt more quickly to changes in the market and seize new opportunities. It is a strategic imperative and smart move.
Brand Reputation
Demonstrating a commitment to accessibility positions your company as a socially responsible organization that values inclusivity, diversity, and equal access to digital resources.
Better User Experience
Features such as captioning, alt text for images, and clear navigation improve user experience for all people. User-friendly interfaces lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased engagement.
Increased market share
People with disabilities travel, eat out, shop, and use digital services every day. By including accessibility features, you reach 10–15% more potential customers.
Legal compliance
Following accessibility standards reduces the risk of legal action, fines, or reputational damage.
Boosted SEO
Accessible websites often rank higher in search results. Google’s mission is “to make the world’s information universally accessible and useful.”
Future-Proofing
Digital inclusion helps build stronger, more flexible products and organizations. It makes your business ready for future market and technology changes.
Brand Reputation
Accessible design shows your company values inclusion, diversity, and equal access to technology.
Better User Experience
Features such as captions, alt text, and clear navigation improve usability for everyone. Accessible interfaces lead to higher satisfaction and stronger engagement.
€12 trillion is held in annual disposable income worldwide by people with disabilities, their families, friends, advocates, and caretakers.
What we do
Accessibility is not an add-on — it’s part of our process from design to deployment. Our accessibility services include comprehensive accessibility audits, user testing, and design consultations that ensure inclusivity from the start.
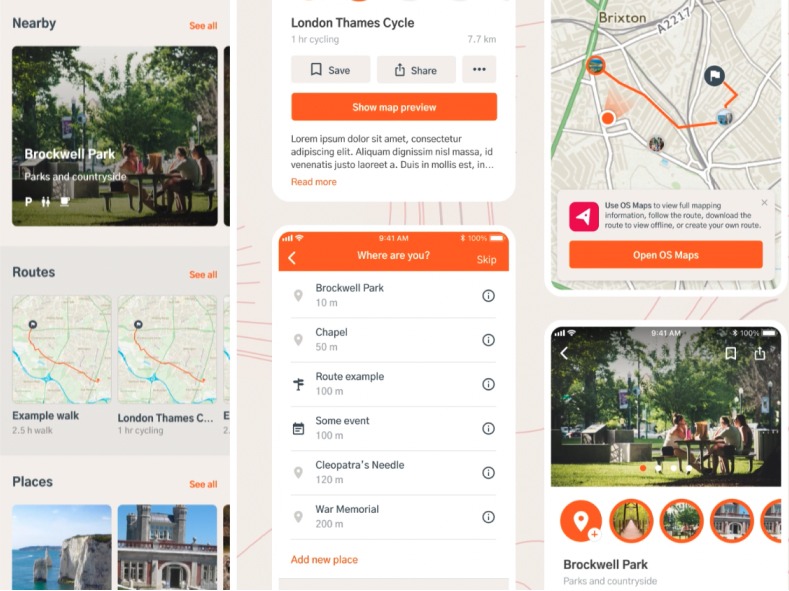
Web & mobile app design
We design with accessibility in mind, our approach to support accessibility and help everyone have a great experience, regardless of their capabilities. Every feature and interaction is tested to make sure it works for all users.
User testing
We test our designs with real users with disabilities. This reveals usability issues that automated tools often miss — and improves the experience for everyone.
Accessibility audits
We review websites and apps against WCAG 2.2 and ADA standards. It is a combination of automated tools, that can identify only 30-40% of the problems, and manual checks by experts that find the rest.
Development
Accessibility should be built into every line of code. Developers must posses accessibility expertise to catch errors and correct them immediately. Proper HTML structure and semantic markup make content easier to read and navigate.
We leverage the expertise of human efforts and AI technology to ensure comprehensive evaluations.
Human-Controlled
Manual testing is essential to ensure full compliance with the WCAG standard. Skilled testers identify accessibility issues that may not be caught by automated tools and provide a more comprehensive evaluation.
AI-Augmented
AI supports human testers by speeding up repetitive checks and reducing human error. Together, they make accessibility reviews faster and more reliable.
Understanding different types of disabilities
Visual
blindness, low vision, color blindness
Neurological
epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, parkinson's disease, speech disabilities and disorders
Hearing
deafness, hard of hearing
Psychiatric
anxiety disorders, depression
Motor and Mobility
paralysis, cerebral palsy, arthritis, amputations
Aging-Related Disabilities
age-related vision and hearing loss
Cognitive
dyslexia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorders (ASD)
Age-Related Mobility Issues
arthritis, decreased muscle strength
Post Covid Syndrome
tiredness or fatigue, difficult thinking or concentration, dizziness
Visual
blindness, low vision, color blindness
Neurological
epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, parkinson's disease, speech disabilities and disorders
Hearing
deafness, hard of hearing
Psychiatric
anxiety disorders, depression
Motor and Mobility
paralysis, cerebral palsy, arthritis, amputations
Aging-Related Disabilities
age-related vision and hearing loss
Cognitive
dyslexia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), autism spectrum disorders (ASD)
Age-Related Mobility Issues
arthritis, decreased muscle strength
Post Covid Syndrome
tiredness or fatigue, difficult thinking or concentration, dizziness

Let's create a more inclusive and user-friendly digital experience together.
.png)
.png)

Including a text transcript makes your video more available to search engines.
Automated accessibility testing is not enough — even the best automated tests can only catch about 25% of accessibility issues.
15% of the world’s population has some sort of disability.
90% of websites are inaccessible to people with disabilities who rely on assistive technology.
Retailers were cited the most in digital accessibility lawsuits (77.55% ), with food service companies in second place at 7.77%
Two-thirds of e-commerce transactions are abandoned by people who are blind because of lack of accessibility.
Frequently
asked questions
What are the 4 web content accessibility principles?
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines, or WCAG, is a set of globally accepted standards that give businesses a clear starting point from which to build inclusive websites that are accessible to all users. WCAG compliance standards are built on four key principles that aim to address every aspect of the online user experience. They are:
-
Perceivable: The information on your website should be presented to users in a way that can be easily perceived. This means ensuring that your text is easily readable, that your multimedia components have alternatives, and that your web design is clear and responsive.
-
Operable: All the components of your website and your user interface should be easy-to-use with a variety of tools. The interface should not require any interaction that a user with disabilities cannot perform, for example, single-mode inputs, complex interactive elements, or timed elements.
-
Understandable: The information presented on your site should be easily understandable to all users. This means designing simple processes, increasing the predictability of various on-site actions, and offering input assistance for users.
-
Robust: Your website should be able to be dependably interpreted by a wide variety of users, including those using assistive technologies.
What products and services does the European Accessibility Act apply to?
The EAA covers commonly used hardware and software products, as well as various
services related to communication, commerce, finance, education, and transportation.
These include:
-
Websites and mobile apps of covered entities
-
Computers and operating systems
-
Smartphones
-
Self-service devices such as ATMs and ticketing machines
-
E-books and e-readers
-
E-commerce experiences
-
Communication technology and equipment
-
Banking services
-
Passenger transport services
-
Audiovisual media services, including broadcast and digital TV and related equipment
What is assistive technology?
Assistive technologies, sometimes referred to as adaptive technologies or rehabilitative devices, promote greater independence for individuals with disabilities by changing how these individuals interact with technology. For example, speech recognition software allows users with hand mobility issues to interact with a computer using voice commands rather than manipulating a mouse and keyboard. Other assistive technologies include alternative input devices, screen magnifiers, and screen reading software.